Download:
Resumen:
Es crucial entender los efectos espaciales de factores relevantes en las variaciones de precios de vivienda, especialmente en el contexto de imperfecciones del mercado. Sin embargo, pocos estudios han aplicado métodos como el modelo de precios hedónicos en países en desarrollo. Este estudio compara modelos de regresión tanto no espaciales como espaciales para examinar los factores asociados con los precios de vivienda basados en los conjuntos de datos de avalúos municipales e inmobiliarios para la ciudad de Quito, Ecuador. Se investiga un conjunto de 17 variables que incluyen características estructurales, de vecindario y de ubicación utilizando un modelo de regresión lineal tradicional y un modelo de Regresión Geográficamente Ponderada (GWR). Los resultados sugieren que, en comparación con el modelo de regresión tradicional, el modelo GWR es más efectivo para capturar las variaciones del mercado inmobiliario a escala detallada. Además, revela hallazgos interesantes sobre los efectos espacialmente variables, a veces opuestos, de algunos atributos de vivienda en los precios en diferentes áreas de la ciudad, lo que sugiere el impacto potencial de la segregación.
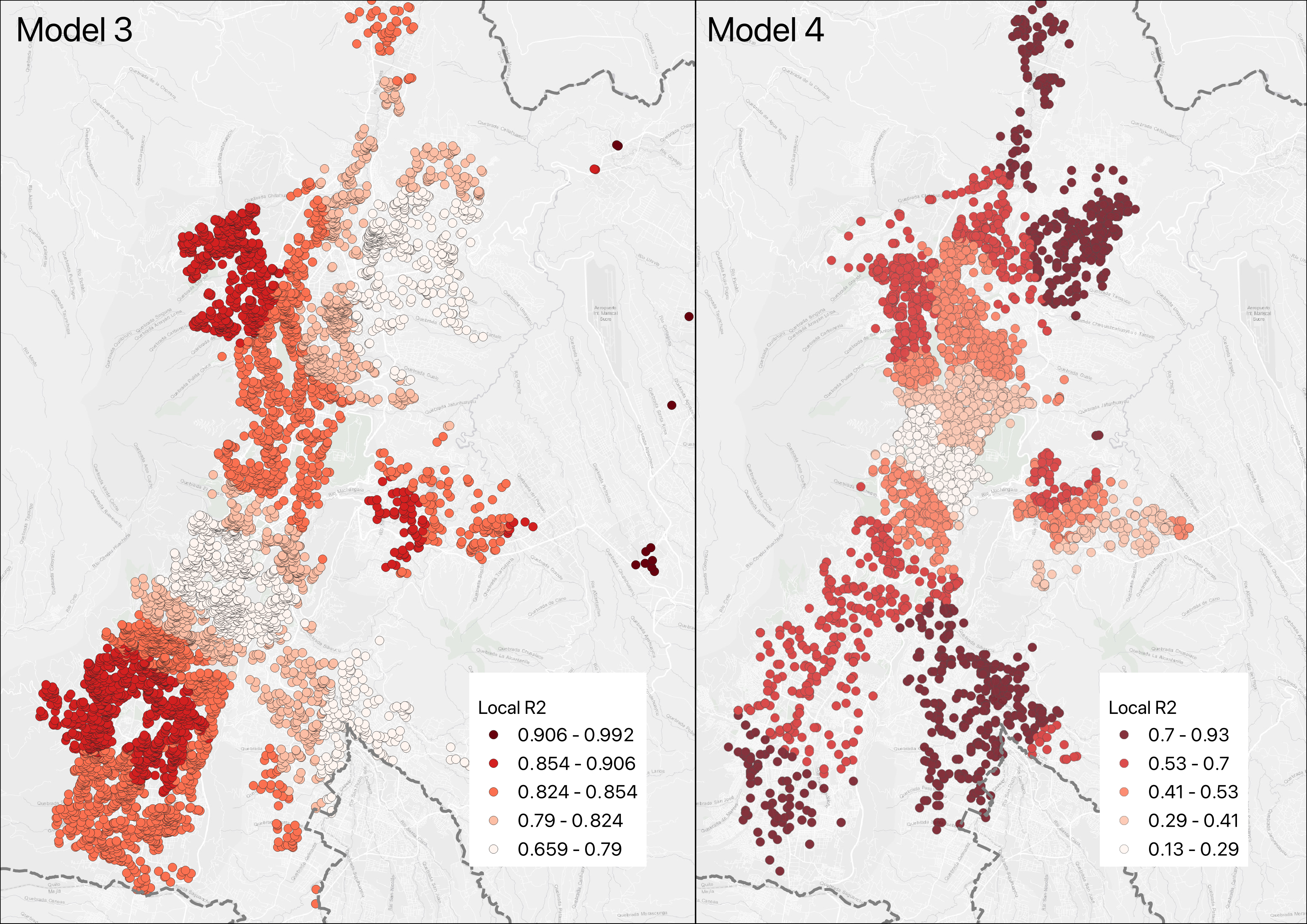
Figure 2: Distribución del R2 local
Citar
Valdez Gómez de la Torre, F.M. and Chen, X. (2024), “Housing price determinants in Ecuador: a spatial hedonic analysis”, International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHMA-09-2023-0121 .
@article{VC24,
author = {Felipe Valdez and Xuwei Chen},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHMA-09-2023-0121},
journal = {International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis},
number = {Issue},
pages = {XXX--YYY},
title = {Housing price determinants in Ecuador: a spatial hedonic analysis},
volume = {ahead-of-print},
year = {2024}}